Hey there! Have you ever wondered how competition for food influences natural selection? It’s a fascinating topic that delves into the intricate relationships between species and their environments. So, let’s dive in and explore the captivating world of natural selection and how it is shaped by the competition for food.
In the wild, survival is often a matter of life or death. And when it comes to finding enough food to sustain themselves, different species must compete with one another for limited resources. This competition for food plays a crucial role in shaping the process of natural selection.
You see, in any given environment, there is a finite amount of food available. As a result, only those individuals within a species who are best adapted to obtain and utilize that food will have a higher chance of survival and reproduction. This means that individuals with traits that give them an advantage in finding or capturing food, such as sharp claws or keen senses, are more likely to pass on their genes to the next generation. Over time, this leads to the gradual evolution of populations, as advantageous traits become more prevalent.
So, whether it’s a predator stalking its prey or a plant competing for sunlight, the struggle for food is a driving force behind the process of natural selection. It’s a constant battle that shapes the incredible diversity of life we see around us. So, let’s delve deeper into this captivating topic and discover the fascinating ways in which competition for food influences natural selection.
Competition for food plays a crucial role in influencing natural selection. In an ecosystem, organisms compete with each other for limited resources like food. Those individuals with traits that give them an advantage in obtaining food are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on these advantageous traits to their offspring. Over time, this leads to the evolution of populations that are better adapted to their specific environments. This process is known as natural selection, where competition for food acts as a driving force for evolutionary change.
How Does Competition for Food Influence Natural Selection?
Food competition plays a crucial role in shaping the process of natural selection. As organisms compete for limited food resources, certain traits and characteristics become advantageous for survival and reproduction. This leads to the selection and inheritance of these favorable traits, ultimately driving evolutionary change. In this article, we will explore the intricate relationship between competition for food and natural selection, highlighting how it influences the evolution of species.
The Role of Competition in Natural Selection
Competition for food is a fundamental aspect of the natural world. Within any given ecosystem, there are limited resources available to support the population of organisms. As a result, individuals must compete with one another for access to these resources, including food. The competition can be intense, with individuals vying for the same food sources and striving to secure enough sustenance to survive and reproduce.
In this struggle for survival, individuals with advantageous traits have a higher chance of obtaining food and outcompeting others. These advantageous traits may include physical adaptations, such as specialized feeding structures or efficient hunting techniques. They may also involve behavioral traits, such as the ability to detect and capture prey more effectively. Over time, individuals with these advantageous traits are more likely to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation, leading to the spread of these traits within the population.
Adaptations for Obtaining Food
The competition for food drives the evolution of specialized adaptations that enhance an organism’s ability to obtain and utilize resources. For example, in predator-prey relationships, predators often develop specific anatomical features or hunting strategies to increase their success in capturing prey. This can include sharp claws, strong jaws, or keen senses that enable them to detect and pursue their food source effectively.
On the other hand, prey species may evolve defensive adaptations to avoid being captured. Camouflage, mimicry, and the development of toxins are just a few examples of strategies employed by prey organisms to deter predators and increase their chances of survival. These adaptations are a direct result of the competition for food and the selective pressures it exerts on both predator and prey populations.
In addition to physical adaptations, behavioral traits also play a significant role in obtaining food resources. For example, certain species of birds may engage in complex foraging behaviors, such as tool use or cooperative hunting, to access food sources that would otherwise be inaccessible. These behavioral adaptations are honed through competition for limited food resources and can greatly enhance an individual’s chances of survival and reproductive success.
Overall, the competition for food drives the development of specialized adaptations that allow organisms to effectively obtain and utilize resources. Through the process of natural selection, individuals with advantageous traits are favored, leading to the evolution of species that are well-adapted to their specific ecological niche.
The Effects of Food Competition on Population Dynamics
Competition for food not only shapes the traits and adaptations of individual organisms but also influences population dynamics. The availability and distribution of food resources can have a profound impact on population size, density, and distribution patterns.
When food resources are abundant, populations can grow rapidly as individuals have access to plentiful sustenance. This can lead to increased competition within the population, as more individuals vie for the same resources. Over time, this competition may drive the evolution of even more specialized adaptations and behaviors that allow individuals to exploit different niches within the ecosystem, reducing direct competition.
Conversely, when food resources become scarce, competition intensifies, and populations may decline. Individuals that are better suited to locate and utilize limited food sources have an advantage and are more likely to survive and reproduce. This can result in the selection of individuals with traits that enable them to extract maximum nutrition from limited resources or to switch to alternative food sources.
The effects of food competition on population dynamics are complex and can vary depending on the specific ecological context. However, it is clear that competition for food plays a central role in shaping the size, composition, and behavior of populations, ultimately influencing the process of natural selection.
Competition and Coexistence
In some cases, species that occupy the same ecological niche may coexist despite competing for the same food resources. This phenomenon, known as resource partitioning, involves the division of resources and habitats between different species to reduce direct competition. Through resource partitioning, species can specialize in different aspects of resource utilization, allowing them to coexist in the same ecosystem without driving each other to extinction.
Resource partitioning can occur through various mechanisms. For example, species may evolve different feeding strategies or preferences, targeting different types of food sources within the same habitat. They may also occupy different microhabitats or utilize resources at different times, effectively reducing competition for food.
Overall, competition for food drives the evolution of specialized adaptations, influences population dynamics, and can lead to the coexistence of species through resource partitioning. Understanding the intricate relationship between competition for food and natural selection is crucial for unraveling the complexities of evolution and the diversity of life on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, competition for food is a driving force behind the process of natural selection. As organisms vie for limited resources, those with advantageous traits have a higher chance of survival and reproduction, leading to the spread of these traits within the population. The competition for food shapes the evolution of specialized adaptations and behaviors that enhance an organism’s ability to obtain and utilize resources. It also influences population dynamics, driving changes in population size, density, and distribution patterns. By understanding the role of competition for food in natural selection, we gain insights into the mechanisms that drive evolutionary change and the diversity of life on our planet.
Key Takeaways: How Does Competition for Food Influence Natural Selection?
- Competition for food can drive natural selection as organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce.
- In a competitive environment, organisms with adaptations that help them obtain food more efficiently have a better chance of survival.
- Competition can lead to the development of specialized feeding behaviors or physical characteristics that give certain organisms an advantage over others.
- Natural selection favors individuals that can outcompete others for limited food resources, leading to the evolution of traits that enhance their ability to acquire food.
- Competition for food can also lead to resource partitioning, where different species evolve to use different food sources, reducing direct competition between them.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about how competition for food influences natural selection:
1. How does competition for food affect the process of natural selection?
Competition for food plays a crucial role in the process of natural selection. In any given population, there is a limited amount of food available, and individuals must compete for access to these resources in order to survive and reproduce. Those individuals who are better adapted to obtain and utilize food have a higher chance of survival and passing on their genes to the next generation. This leads to the gradual accumulation of advantageous traits related to foraging, such as increased speed, agility, or specialized feeding mechanisms.
Over time, natural selection favors individuals with traits that give them a competitive edge in obtaining food. This creates a constant pressure for individuals to adapt and evolve in response to changes in their food environment. For example, if a new food source becomes available, individuals with the genetic variation necessary to exploit this resource more efficiently may have a higher chance of survival and reproductive success, leading to the spread of these advantageous traits throughout the population.
2. How does competition for food drive evolutionary changes?
Competition for food is one of the main driving forces behind evolutionary changes. When resources are limited, individuals who are better adapted to obtain or utilize food have a higher chance of survival and reproductive success. This leads to the gradual accumulation of beneficial traits related to foraging and resource acquisition.
For example, imagine a population of birds that primarily feed on insects. If the population experiences increased competition for insects due to a rise in population size or a decrease in insect abundance, individuals with traits that enhance their ability to locate and capture insects will have a higher chance of survival. These individuals may have longer beaks, sharper claws, or superior hunting strategies. As a result, these advantageous traits become more prevalent in the population over time, driving evolutionary changes.
3. How does competition for food influence genetic variation?
Competition for food can influence genetic variation by selecting for individuals with certain genetic traits that provide an advantage in obtaining food. When individuals with advantageous traits have a higher chance of survival and reproductive success, their genes are more likely to be passed on to the next generation. This can lead to an increase in the frequency of specific genetic variations within the population.
Additionally, competition for food can also lead to the development of new genetic variations through mutation and genetic recombination. Mutations are random changes in DNA that can result in new traits. If a mutation provides an advantage in obtaining food, individuals carrying this mutation may have a higher chance of survival and reproduction, leading to the spread of the new genetic variation within the population.
4. Can competition for food lead to speciation?
Competition for food can contribute to the process of speciation, which is the formation of new species. When populations become isolated from each other and experience different food availability or competition levels, natural selection can act independently in each population, driving them to evolve in different directions.
Over time, the accumulation of genetic differences related to food acquisition and utilization can lead to reproductive isolation between the populations. This means that individuals from one population are no longer able to successfully mate with individuals from the other population. As a result, they become reproductively isolated and may eventually become distinct species.
5. Are there any examples of competition for food influencing natural selection?
Yes, there are numerous examples of competition for food influencing natural selection. One well-known example is the evolution of the long neck in giraffes. In environments where food is scarce and located high off the ground, giraffes with longer necks have a competitive advantage as they can reach leaves that other herbivores cannot. Natural selection favors individuals with longer necks, and over time, giraffes have evolved to have exceptionally long necks to access their primary food source.
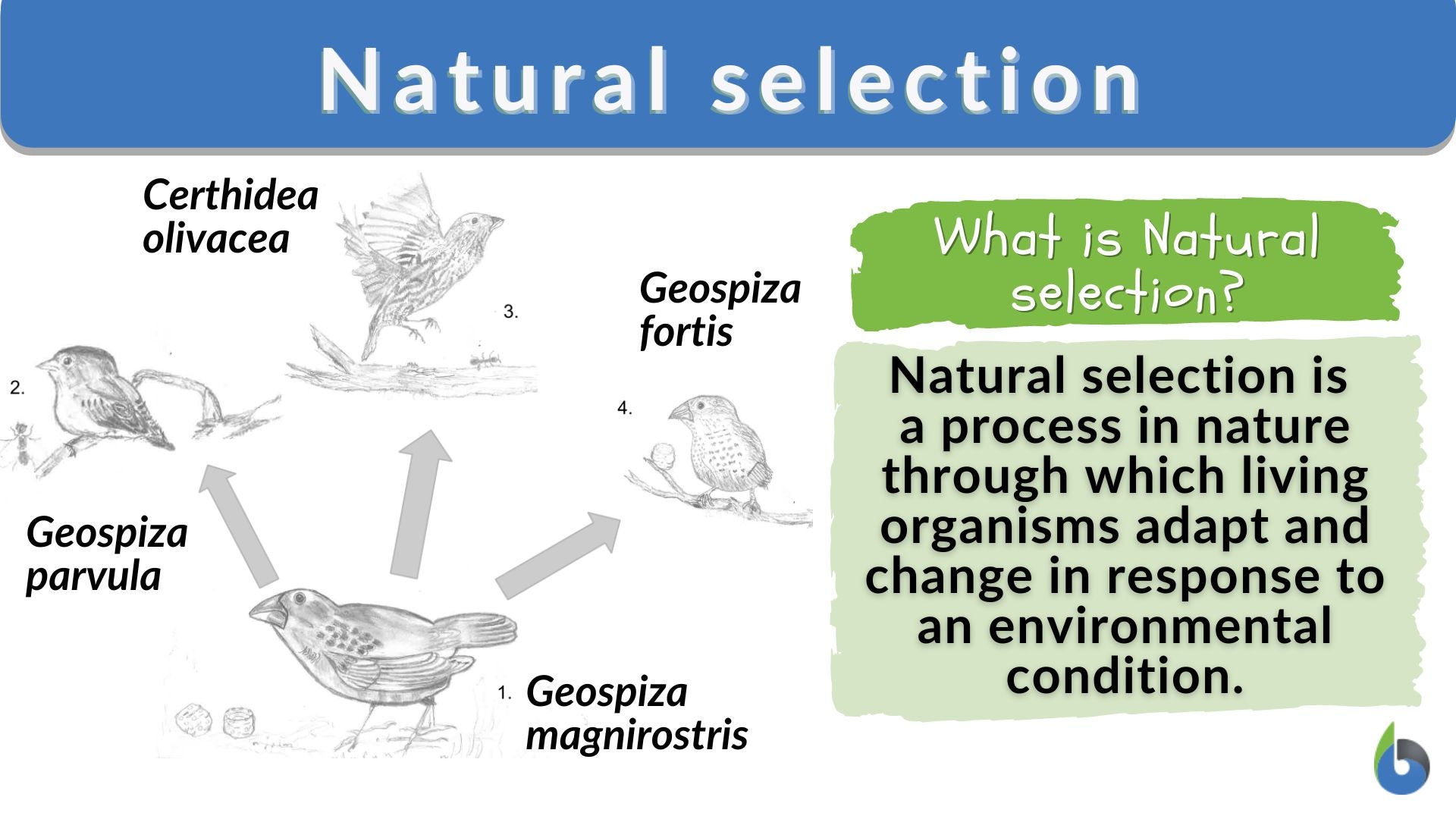
Another example is the evolution of beak size and shape in Darwin’s finches. Different species of finches on the Galapagos Islands have adapted to exploit different food sources, such as seeds, insects, or nectar. The variations in beak size and shape among the finch species are the result of natural selection acting on individuals with traits that allow them to efficiently obtain their specific food source.
Final Thought: How Does Competition for Food Influence Natural Selection?
As we delve deeper into the fascinating world of natural selection, it becomes clear that competition for food plays a crucial role in shaping the evolutionary process. When individuals within a species are vying for limited resources, such as food, a dynamic interplay begins to unfold, driving the forces of natural selection. Through this intense competition, only the most fit and well-adapted individuals are able to secure enough sustenance to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to future generations.
The influence of competition for food on natural selection cannot be understated. It acts as a powerful mechanism for driving the evolution of various traits, from physical adaptations to behavioral strategies. Individuals who possess advantageous traits, such as efficient foraging techniques or the ability to access unique food sources, are more likely to thrive in competitive environments. Over time, these advantageous traits become more prevalent in the population, as individuals without them struggle to secure the necessary resources for survival.
In conclusion, the impact of competition for food on natural selection is undeniable. It serves as a driving force behind the evolution of species, shaping their physical and behavioral characteristics. As individuals adapt to overcome the challenges posed by limited resources, the fittest among them emerge victorious, perpetuating their advantageous traits. Understanding the intricate relationship between competition and natural selection grants us valuable insights into the complex web of life and the remarkable ways in which organisms adapt to their environments.
